50
|
CERECDOCTORS.COM
|
QUARTER 1
|
2016
| | |
VALCANAIA, NEIVA, FASBINDER
Fig. 6 Biocopy and proposals
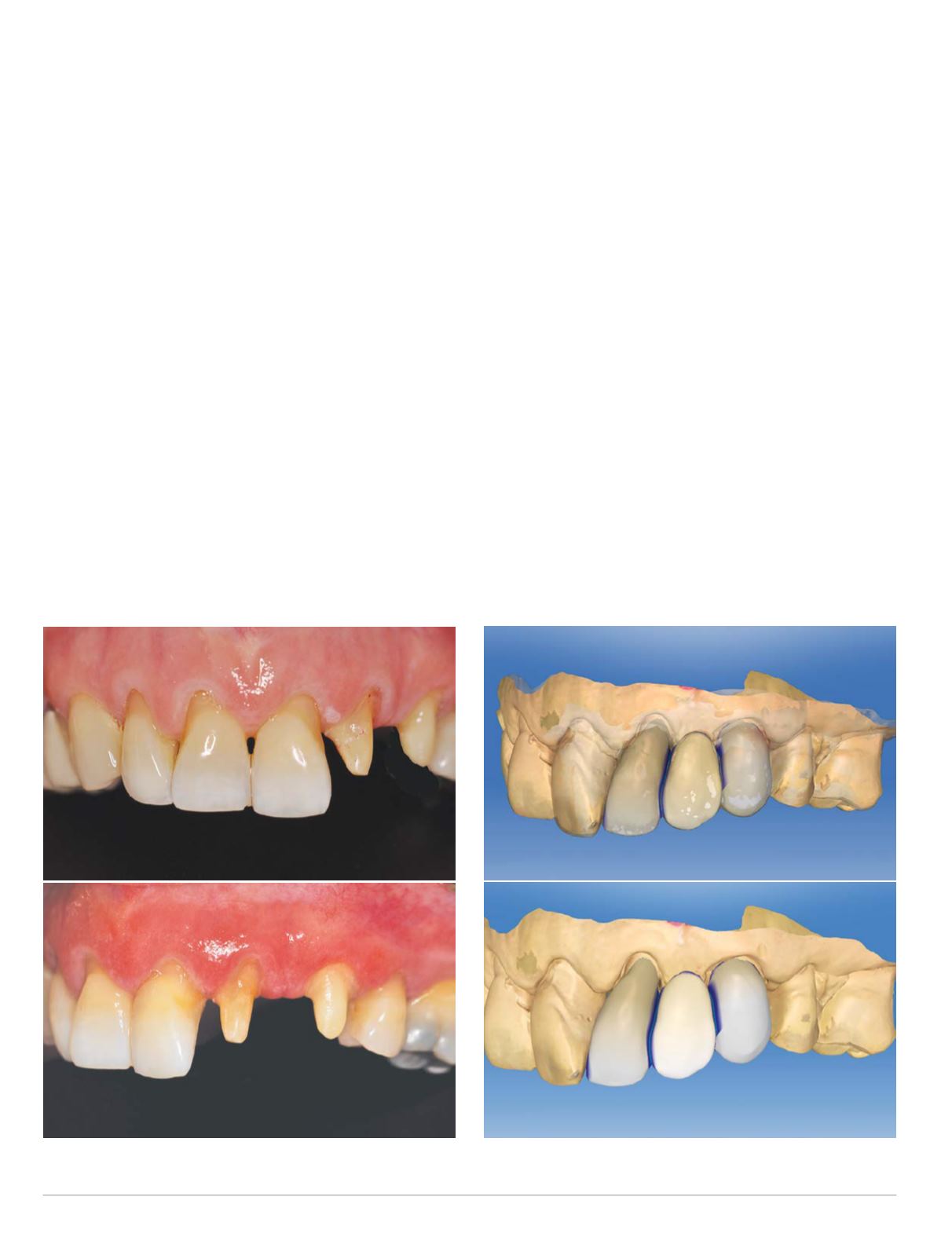
Fig. 5 Preparations
create space for the additional width of the pontic space (Fig. 5).
A polyvinylsiloxane impressionwas made of the final preparations
and maxillary dentition. This was to provide a master model for
fitting and refinement of the milled FPD, as it was not planned to
be done chairside due to the additional time required for milling
and processing the FPD.
The maxillary and mandibular arches were scanned using
CEREC Omnicam with software version 4.3. The Biocopy design
mode was used to reproduce the diagnostic prototype in the final
design of the full contour FPD (Fig. 6). This allowed for replication
of the desired distribution of tooth proportions and emergence
profile created in the prototype. The length of the tooth prepara-
tions was a significant aid in creating connector sizes >16 mm2 as
recommended by themanufacturer (Fig. 7). This was aided by also
flattening the lingual contours of the FPD. Once the proportions
and occlusal relationships were verified, the FPD was milled from
lithium disilicate (e.max CAD; shade D2LT) and then contoured
(Fig. 8). The restoration was finished and crystallized prior to final
shade customization (Fig. 9).
The patient returned for delivery of the e.max CAD FPD. The
provisional FPD was removed, the preparations were cleaned of
temporary cement, and the e.max CAD FPD was trial seated to
verify margin fit and proximal contact. The gingival tissue around
tooth #10 showed significant signs of improvement with only
a mild hyperkeratinized area remaining on the papilla mesial to
tooth #10 (Fig. 10). A chairside correction firing was performed to
create the hypo-calcifications on the contralateral teeth. In order
to reduce the translucency of the enamel in the incisal one-third, a
wash of crystal glaze and crème was applied. A wash of white was
applied to create the hypocalcified areas, preferentially on #10.
Olive with a little mahogany was applied to the connector areas
to delineate the abutments from the pontic to avoid altering the
thickness of the connectors (Fig. 11).
The FPD was tried in one additional time, and the patient was
very satisfied with the final esthetic result achieved with chair-
side shade customization (Fig. 12). The internal aspect of the
abutments were etched with 4.9 percent HFl acid for 20 seconds,
rinsed and dried thoroughly, and then coated with a silane coupler


